Goal Planning - Goal - Part 6
Identify your goals and prioritize them
What are goals ?
As an individual / family, you have a vision or a personal objective/s that you would like to meet in your lifetime .
Some / all of these objectives may need to be financed . Therefore having a goal makes sense.
- Goals have to be SMART .
- Create a plan to achieve your goal
- Execute the plan.
- Examine results of your execution.
- Incorporate feedback to your plan
- Repeat steps 3 to 5
In other words, this is your famous Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle that will help you achieve your goal.
REMEMBER : You are the biggest stakeholder in your financial goal and therefore only YOU can achieve your goal.
What do we require in goals ?

Smart Goals
GOAL EXAMPLE : I would like to own an SUV costing Rs 20,00,000/- when I am 35 .
If you take the above goal, you have clearly laid out your goal that you intend to own a car costing 20 lakhs today when you become 35 and it should be a SUV. You can name the SUV later, but this is a good start !
GOAL EXAMPLE : On lifestyle expenses, currently I spend Rs 7,00,000/- per year and I need to take care of retirement, assuming, that I retire at 60 and I would like to leave an estate of 1 crore for my children .
Lifestyle expenses are the recurring expenses that happens in an individual / family’s house. These do not fluctuate significantly and after retirement, there could be one or two expenses that could be added. Moreover, here, the goal clearly states that he plans to retire at 60 and given a life expectancy he would want to take care of that until the event takes place
Parameters for a financial goal
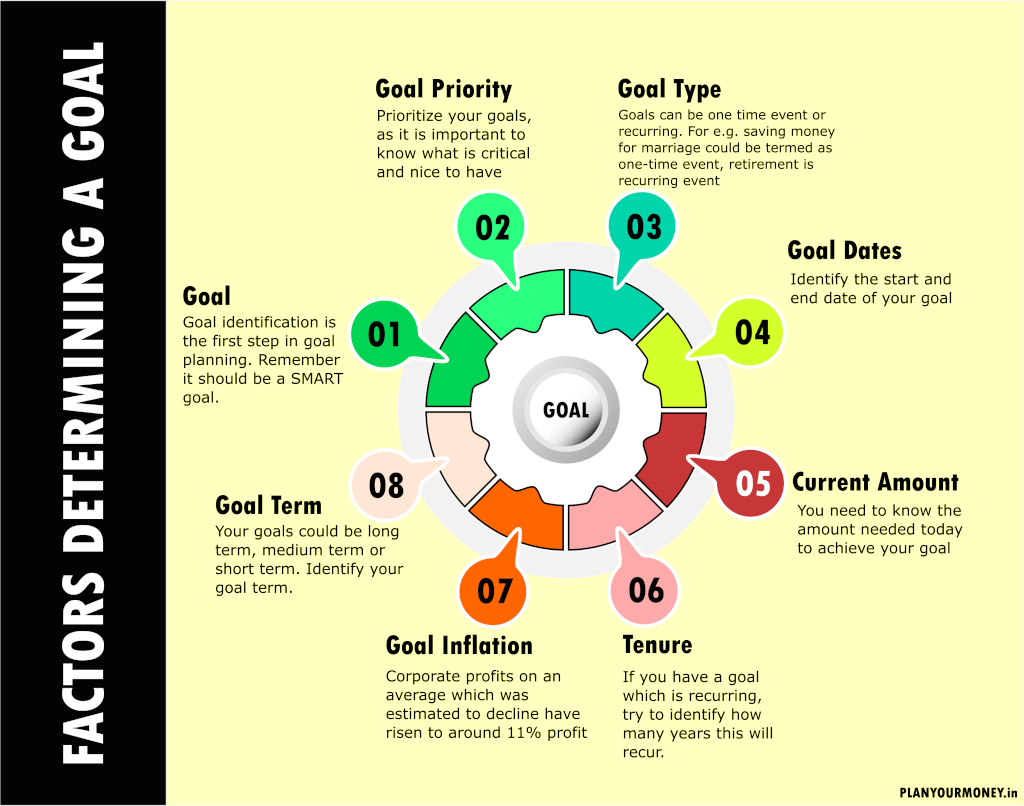
Financial Goal
- Goal : Goal identification is the first step in goal planning. Identify all your goals and make sure you make them SMART .
- Priority : Prioritize your goals. Some of them are CRITICAL , some of them are NICE TO HAVE
- Goal Type : Some goals occur only once in a lifetime (marriage of son), some recur every year (retirement).
- Goal Dates : Identify the Start and End Date of your goal
- Current Amount : How much amount is required to accomplish that goal today ?
- Tenure : If it is a recurring event, how many years does it recur ? for e.g. MBA fees recurs for two years
- Goal Inflation : Inflation erodes purchasing power. School fees increase by 9% on an average. It
- Goal Term : Goal Term could fall in one of these categories Short Term / Medium Term / Long Term. If you plan to retire in 30 years, you could consider it long term
What next ?
- What are the resources available ?
- Can you allocate these resources towards your goals ?
- Are you allocating the right resources towards your goals ? for e.g. long term goals require resources which are long term in nature
- Do you have sufficient time to generate resources and allocate towards the goal ?
- What kind of assets are you allocating towards your goal ?
- Are the assets that you are allocating towards your goal also considering your risk profile ?
Other Links
You can refer to other 5 parts of my Goal Planning series below
- Goal Planning - Overview
- Goal Planning - Risk Profile
- Goal Planning - Assets
- Goal Planning - Liabilities
- Goal Planning - Income and Expenses


